Transmission
Chickenpox is very
contagious.
It spreads by touching or
breathing in the virus
particles that come from the
chickenpox blisters, and
by breathing in the air
surrounding someone with
chickenpox. People with
shingles can also spread the
chickenpox virus to people
who have never had the
disease or the vaccine.
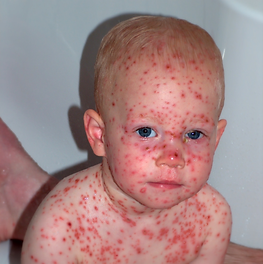
Varicella (Chicken Pox)
Complications
Complications from chickenpox are not very common but it is possible if someone has a weak immune system.
Complications can include:
-
bacterial infections of the skin
-
bleeding problems
-
blood stream infection
-
death
-
dehydration
-
inflammation of the brain
-
pneumonia
Many of the healthy adults who died from chickenpox contracted the disease from their unvaccinated children.
Signs + Symptoms
Anyone who hasn’t had
chickenpox or gotten the
chickenpox vaccine can get
the disease.
Symptoms can include:
-
fever
-
headache
-
itchy, blistery rash
-
loss of appetite
-
fatigue
Treatment
Vaccine schedule for children 0-6
Chickenpox is treated with antiviral medication. The itchy rash may be soothed with calamine lotion and it is important to keep fingernails trimmed short to prevent skin infections caused by scratching the blisters.
2 vaccines between 12-15 months and 4-6 years.
Source: Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.

